technological innovation
The influence of raw materials, temperature and guide plate on the quality of wedge rolling products and technological countermeasures
In the 1960s, the former Czechoslovakia invented wedge rolling technology, and the technology was applied to the production of shaft and hardware tools. In 1979, the team of academician Hu Zhenghuan of the University of Science and Technology Beijing successfully used the wedge rolling technology for the production of hardware tools, officially opening the road to industrialization. After more than 40 years of development, wedge rolling process has achieved great success in shaft precision forming, long bar forging forging and so on, and has played the advantages of high efficiency, material saving and energy saving. It is widely used in automobile, agricultural machinery, construction machinery, hardware tools and other fields, especially the gear shaft and camshaft of the automobile industry.
After 2010, with the rapid development of the automotive industry, customers are increasingly demanding the quality of product delivery. In the production process of cross wedge rolling, due to the abnormal factors such as raw materials, heating temperature and guide plate, the product may appear folding, loose, stuck material, overheating, overburning, size inconsistency, scratches, deep pits and other defects. These defects not only adversely affect the quality, but also restrict the stability of production and affect the delivery of orders. How to eliminate these quality defects and improve production stability is particularly important. This paper will analyze the impact on product quality from three aspects: raw materials, temperature and guide plate, and put forward effective process countermeasures.
The influence of raw materials on product quality and technological countermeasures
The defects of raw materials that affect the transverse wedge rolling process are mainly divided into two categories: one is the appearance defects of raw materials, such as cracks, folding, pits, uneven end faces, necking, bending, ellipse, etc. The appearance defects of these raw materials will be "inherited" to the surface of the transverse wedge rolling product during plastic forming; The other is the internal defects of raw materials, such as inclusion, porosity, etc., which can also lead to internal defects of wedge-rolled products. Folding and loosening of raw materials are the main factors affecting forgings, and the following is a key analysis.
Material folding
For black steel round steel, there will occasionally be the folding of raw materials, and it is not easy to find in the round steel state. However, after wedge rolling production, it can be obviously seen in hot state, cold state and machining, as shown in Figure 1.
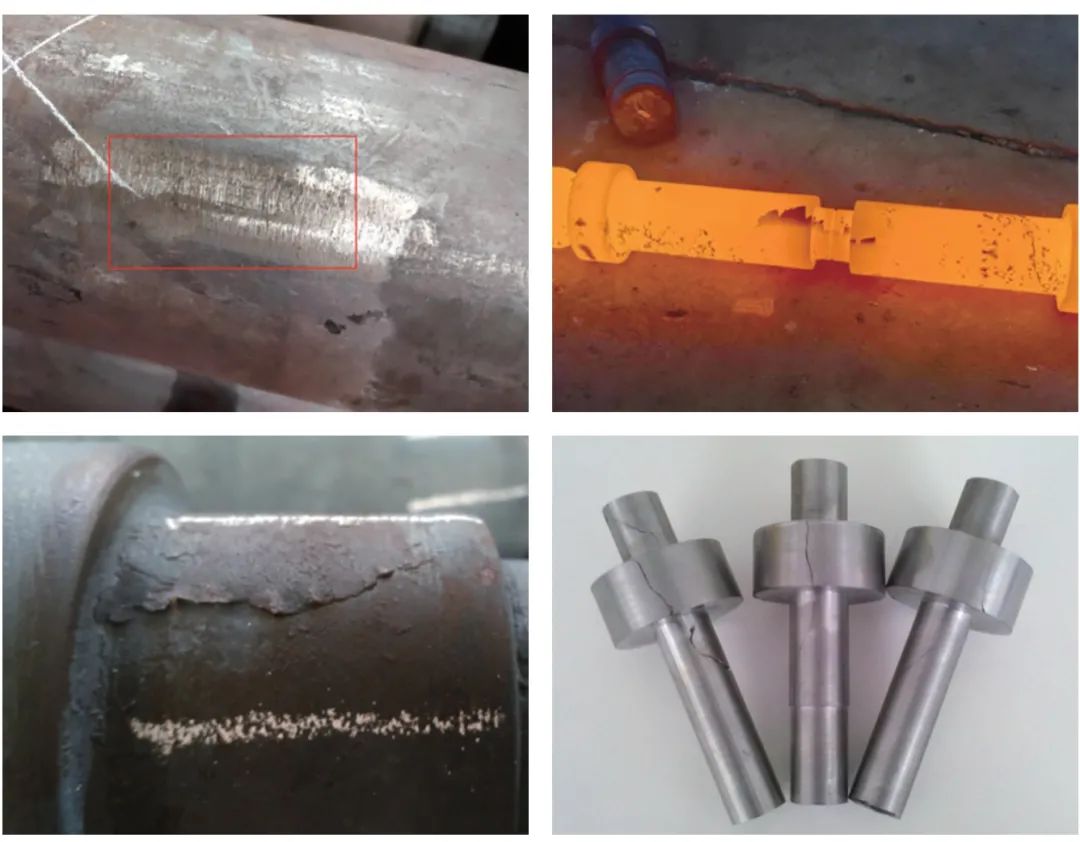

Figure 1 Comparison of raw materials before and after folding and rolling
Measures: Since the folding of raw materials is a defect of hot-rolled round steel, the delivery of bright materials (grinding materials) can be required in the steel agreement to increase the inspection of surface defects. If the cost factor is considered and black leather material is used, 100% appearance inspection of the hot shaft should be carried out during the production of cross wedge rolling to avoid defects flowing into the next process.
Loose material
Gear and gear shaft are the core components of automobile transmission, which require high mechanical properties such as core strength, flexural resistance and torsion resistance, impact toughness, etc. Generally, hot-rolled round steel is used.
In the continuous casting process of hot rolled gear steel, due to the factors of fast drawing speed and high superheat, it is easy to cause shrinkage and loose defects in the casting billet. In the subsequent hot rolling process, if the rolling process parameters such as the initial rolling temperature and rolling ratio are not suitable, the defects of the billet can not be welded, which will lead to loose steel. Generally, steel bar phased array ultrasonic nondestructive testing and low-power tissue and defect acid corrosion testing methods are used for the inspection of loose defects. The situation of steel loose and inspection is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 Loosening and inspection of steel
Measures: wedge rolling process can not improve the situation of steel loose, the use of loose steel, generally will pass defects to wedge rolling products. Therefore, in general, the rolling ratio is not less than 9 in the steel agreement, and the larger rolling ratio can make the deformation of hot rolled steel deep in the heart, improve the defects of the billet, and obtain qualified steel.
Influence of heating temperature on product quality and technological countermeasures
Wedge rolling process to produce shaft parts, generally use medium frequency induction heating, heating temperature and die forging is basically the same, the general requirements of 1100 ~ 1200℃, different materials of steel requirements are different. Heating temperature is too high or too low will lead to stuck material, overheat and overburn, size inconsistency, hollow porosity and other defects. The next part focuses on the analysis of defects such as card material, overheat and overburn, and size inconsistency.
material jamming
When the heating temperature is lower than the process requirements or the rolling mill is not started in a timely manner, causing the hot-state material to be cooled by water, it will result in insufficient rolling force and material jamming, as shown in Figure 3. When the temperature is too high, it leads to a decrease in the deformation resistance of the material, while the rolling mill speed and friction conditions remain unchanged, which can also disrupt the rolling conditions and cause material jamming.
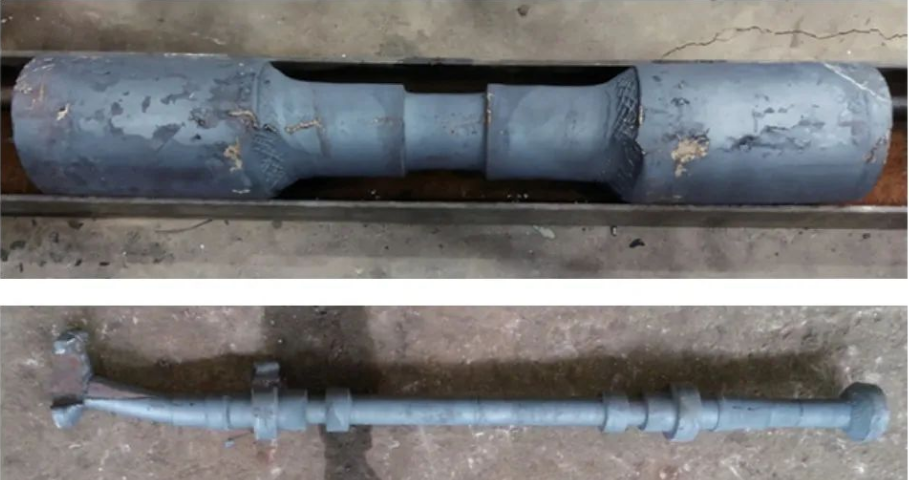

Figure 3: Defective scrap due to material jamming
Measures: Using a temperature measurement probe and an automatic sorting system can effectively address the issue. The temperature measurement probe can measure the temperature of each billet exiting the furnace, and the automatic sorting system can input temperature ranges. If the temperature falls below the lower limit, the billet will be automatically diverted to the low-temperature rack, and if it exceeds the upper limit, the billet will be diverted to the high-temperature rack. Since the intermediate frequency discharge typically utilizes a fast chain to quickly remove the hot billet, there is a certain level of vibration. It is necessary to regularly tighten the temperature measurement probe to avoid positional deviation. Additionally, regular use of a temperature gun for comparison and calibration is required.
Overheating and overheating occur
When the heating temperature exceeds the process requirements or when the material stays at high temperatures for an extended period. This rapid increase in temperature causes the austenite grains to grow excessively, resulting in overheating defects. When the heating temperature of the billet exceeds the overheating temperature, it can also lead to the infiltration of oxidizing gases into the grain boundaries, causing oxidation of intergranular substances such as Fe, C, and S. In severe cases, it can even lead to the melting of grain boundaries, completely destroying the bonding between grains, resulting in overheating defects, as shown in Figure 4.
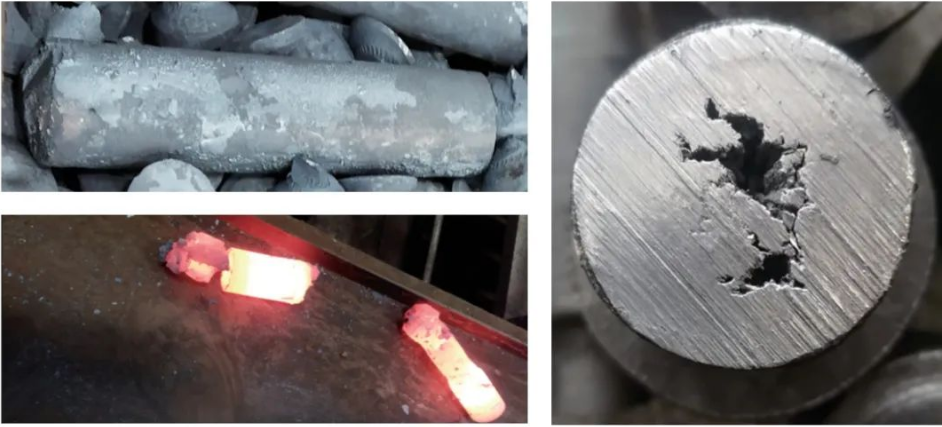

Figure 4: Defective products due to overheating
Measures: It is necessary to strictly follow the heating specifications and use a temperature measurement probe along with an automatic sorting device. For the billets that are sorted out as overheated, they must be scrapped and properly disposed of.
inconsistent dimensions
In the production of axis-like components using wedge cross rolling, symmetric rolling is commonly employed, such as one pass producing two, four, or even six components. For example, when producing four components in one rolling pass, if the billet is relatively long, uneven heating during intermediate frequency heating can result in poor dimensional consistency among the four components and even lead to dimensional deviations, as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5: Inconsistent Axial Dimensions of Large Shafts Due to Uneven Temperatures
For the mid-frequency heating equipment used in cylinder billet push feeding (non-continuous feeding), it is one of the important causes leading to this problem. During the mid-frequency heating process, the billet is heated inside the furnace. When the billet is near or exceeds the furnace opening, it is prone to have a lower temperature at one end. Since the molds for the four components are designed based on the principle of uniform temperature conditions, improper placement of the billet inside the mid-frequency furnace can result in temperature non-uniformity and inconsistent product dimensions.
During mid-frequency heating, when the billet is near or exceeds the furnace entrance or exit, it can cause temperature non-uniformity, as shown in Figure 6(a). To address this issue, it is necessary to adjust the position of cylinder limit switch and the number of billets, ensuring that both the head and tail billets are inside the furnace and at least 50mm away from the furnace opening to avoid rapid cooling and maintain temperature uniformity, as shown in Figure 6(b).
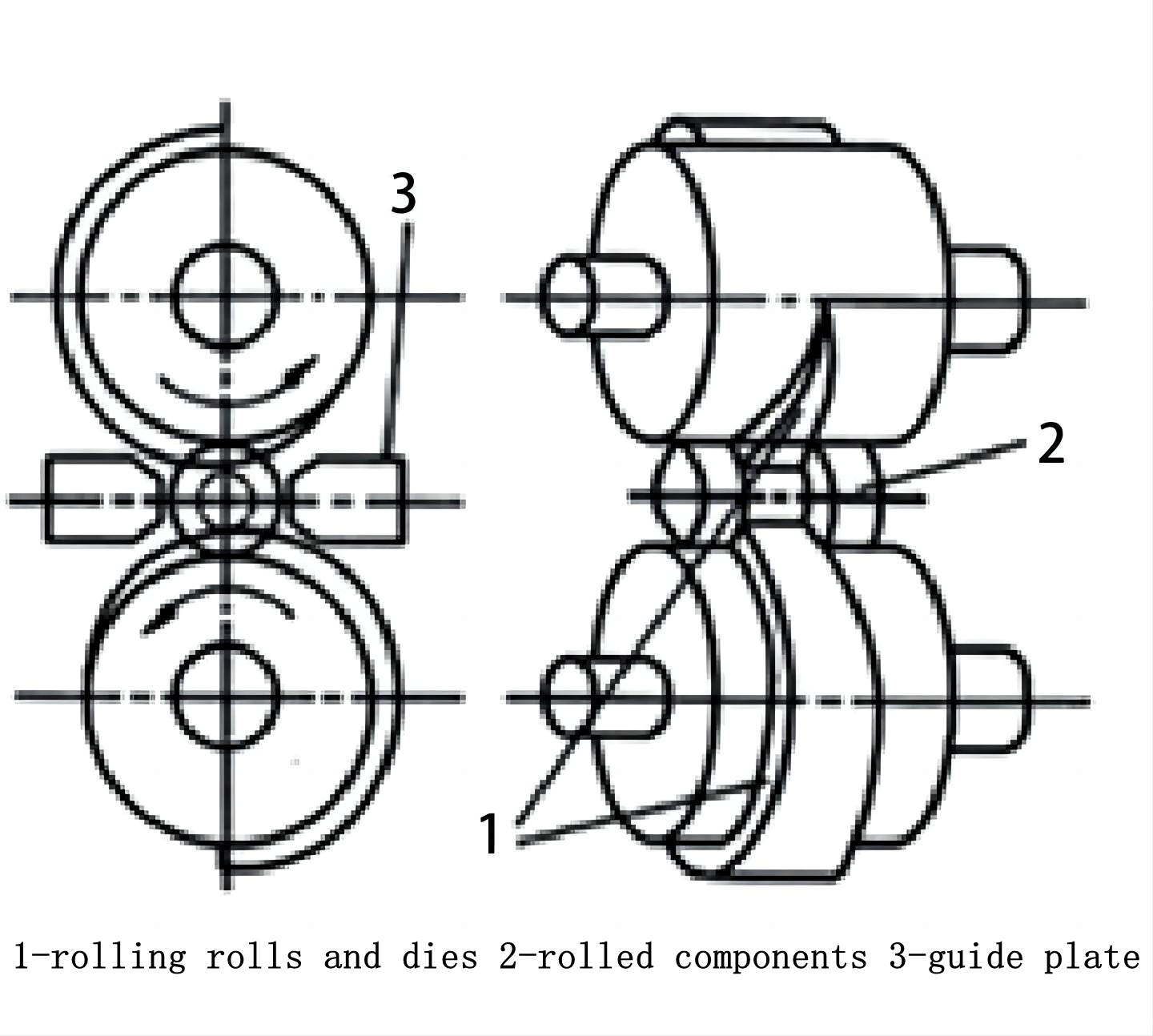
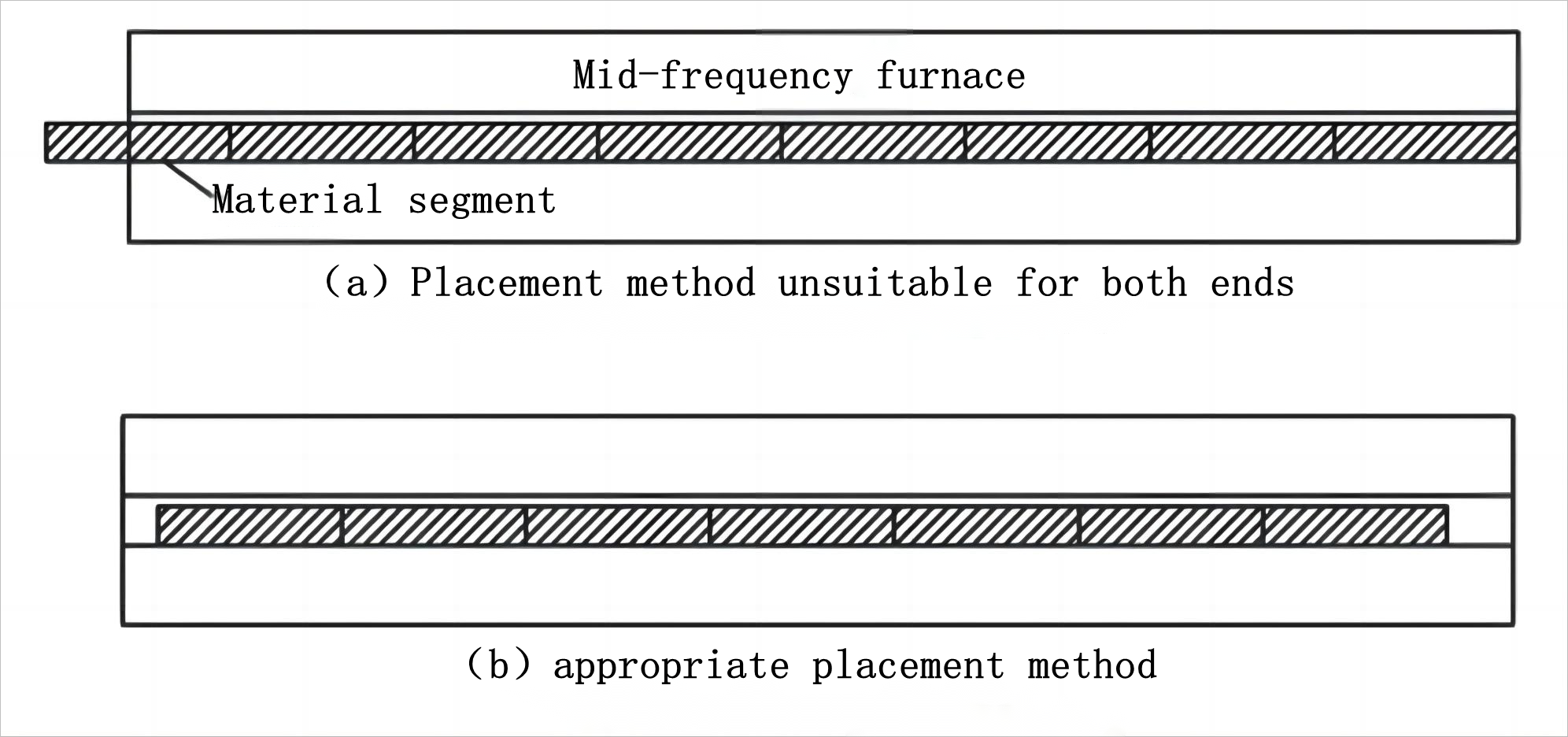
Figure 6: Placement of billets in the mid-frequency furnace
Impact of guide plates on product quality and process measures
The two-roll vertical wedge-cross rolling mill consists of an upper and a lower roll. The upper roll is installed with an upper die, while the lower roll is installed with a lower die. There are two guide plates in the front and rear to control the rolling stock and prevent swinging during production, ensuring a stable rolling process. The positional relationship between the rolling rolls, dies, rolling stock, and guide plates is shown in Figure 7.
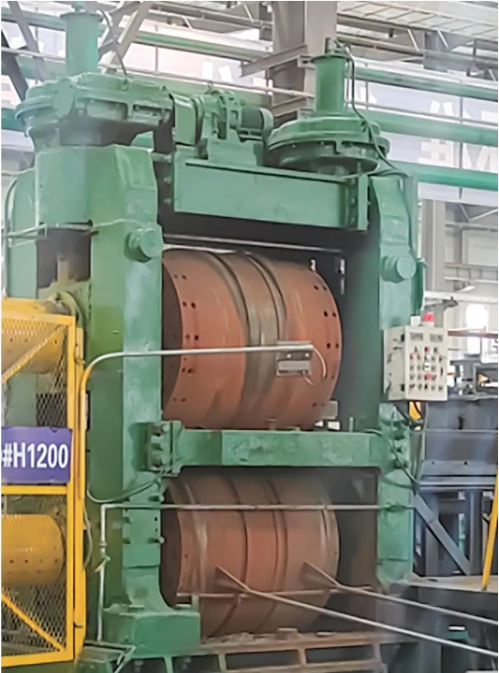

Figure 7: Positional relationship between the rolling rolls, rolling stock, and guide plates.
Scratch defect
A scratch defect refers to a groove-like flaw on the outer surface of a product, typically occurring on the large diameter of the product, as shown in Figure 8(a). Scratches happen during the rolling process when hardened material adhered to the guide plate scratches the rotating hot shaft's outer surface during forming. To prevent material from sticking to the guide plate and causing scratch defects, it is important to avoid the guide plate scraping off the surface material of the hot shaft during plastic forming. In a stable rolling process, the guide plates should be positioned at different horizontal levels, with the outer surface of the shaft placed against the middle section of the guide plate, as illustrated in Figure 8(b).
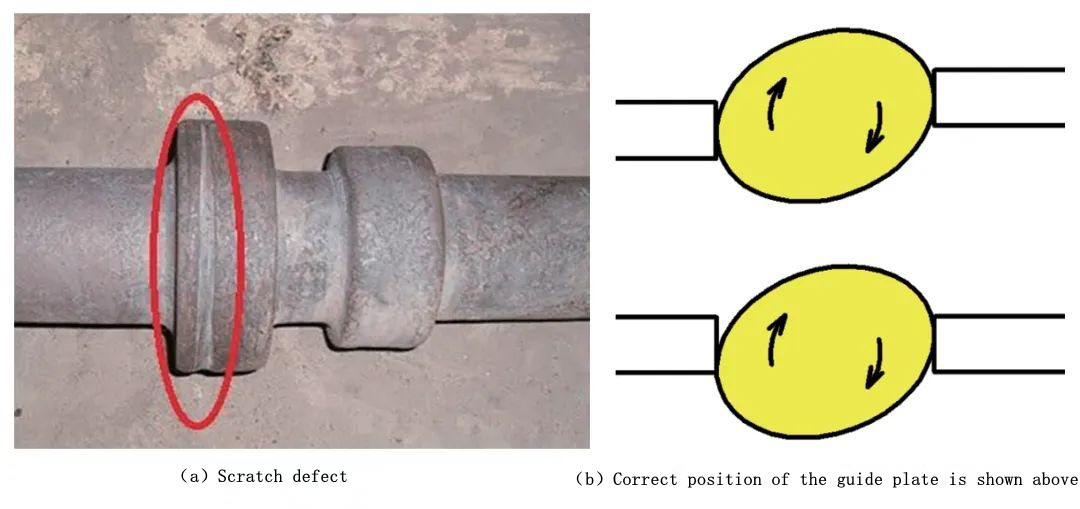
When the height position of the guide plate is improperly adjusted and the outer surface of the hot shaft is close to the upper and lower edges of the guide plate, it can lead to material scraping. In such cases, it is necessary to adjust the height of the guide plate. When the upper and lower dies exert significantly different forces on the rolling stock, causing the hot rolling stock to be tightly pressed against one side of the guide plate and experiencing greater force, it can also result in material sticking to the guide plate and subsequently causing scratches. In this situation, measures such as adjusting the phase, the front and rear positions of the guide plate, and repairing the forming surfaces of the dies should be taken to prevent excessive force exerted on the rolling stock by a single-sided guide plate. Additionally, the surface hardness of the guide plate is also crucial. Based on practical experience, using D322 welding rod for hardfacing and grinding it to a hardness exceeding 60HRC can reduce wear and minimize the occurrence of material sticking situations.
Deep pit defect
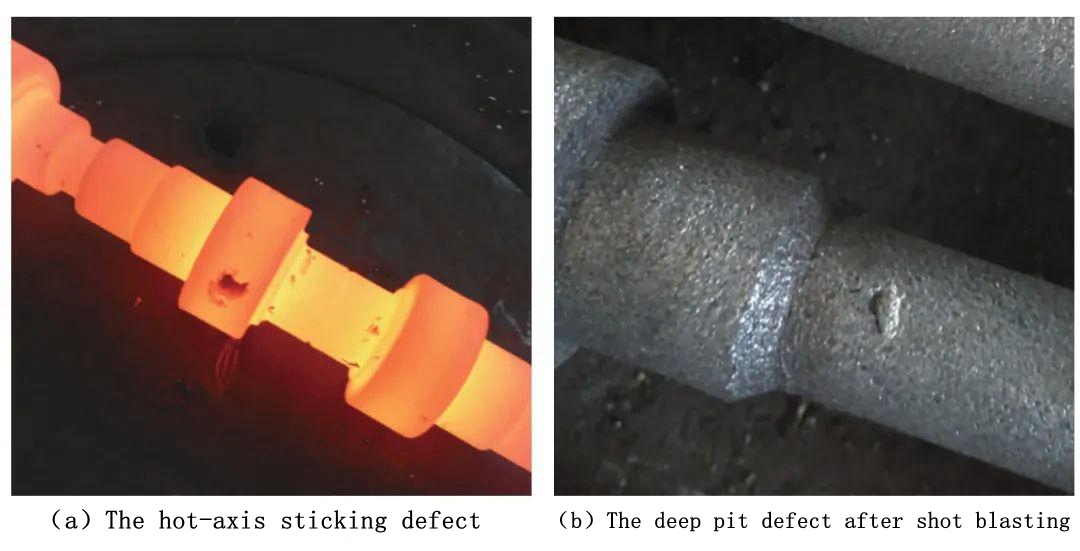
The deep pit defect can occur at any step of the rolling stock and is often revealed after shot blasting. The root cause of the deep pit defect is the same as that of the scratch defect. During the rolling process, continuous water cooling is applied, causing the material sticking to the guide plate to be in a cold state. When the material adhered to the guide plate falls off, it gets pressed into the surface of the hot shaft, as shown in Figure 9(a). Under the action of shot blasting with steel grit, the adhered material on the surface of the shaft will fall off, creating deep pit defects, as shown in Figure 9(b). The solution to this problem is the same as the one for addressing scratch defects: preventing the guide plate from scraping the surface of the hot shaft. Only by avoiding the material being scraped off the hot shaft surface by the guide plate can the deep pit defect be resolved.
Conclusion
This article summarizes the various defects in dimensions, appearance, and internal structure of shafts caused by abnormal parameters of the wedge cross-rolling die. These defects include size deviation, looseness, hollows, ellipticity, skinning, indentations, helical marks, reduction in diameter, edge defects, folding, whirls, and bending. The reasons for these defects are analyzed in detail, and clear optimization methods for die parameters are proposed. These methods effectively control the product quality of the wedge cross-rolling process and strongly promote the promotion and application of this technology.
RELATED NEWS
- Not sure about the T4, T5, and T6 materials of aluminum profiles? This article h 2024-03-20
- How to use aluminum profile section design skills to solve extrusion production 2024-03-19
- Factors affecting the life of trimming and punching molds 2024-03-12
- Overview of Steel/Aluminum Welding Technology 2024-02-29
- Steel belt conveying direction 2023-09-26
CATEGORIES
LATEST NEWS
CONTACT US
Contact: Manager:Miss Jasmien
Phone: +8618825429836
E-mail: info@gdaa-cn.com
Whatsapp:+8618825429836
Add: Headquarter:No.8,Yixian Road,GDAA Mansion,Guangfo Zhicheng, Dali Town,Foshan,Guangdong.China
