News
What are the processing techniques of aluminium alloy?
Aluminium alloy is a commonly used industrial material. It is very light and weighs about one-third of the same volume of copper or steel. It is corrosion-resistant, is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity, reflects light and radiant heat, is non-magnetic, is not easy to absorb neutrons, can be safely used in food and medicine. And it can be formed into various kinds of industrial materials by all known metal processing techniques. Such as aluminium tube, aluminium circle, aluminium sheet, aluminium foil, aluminium coil, aluminium strip, etc. This article will introduce several common aluminium alloy processing techniques.
(1) Classified according to the force and deformation mode of the product
A. Rolling
Rolling is a deformation process in which the ingot is drawn into the rotating rolls by friction, and with the pressure applied by the rolls, the cross-section is reduced, the shape changes, the thickness becomes thinner and the length increases. According to the different rotation directions of the rolls, rolling can be divided into longitudinal rolling, cross rolling and skew rolling.
During longitudinal rolling, the direction of rotation of the work rolls is opposite, and the longitudinal axis of the rolled piece is perpendicular to the axis of the roll. It is the most commonly used method in flat roll rolling of aluminium alloy plates, strips, and foils.
longitudinal rolling
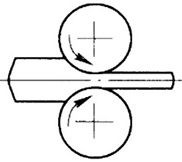
During cross rolling, the direction of rotation is the same, and the longitudinal axis of the rolling piece is parallel to the axis of the roll, which is rarely used in the rolling of aluminium alloy plate and strip.
Cross rolling
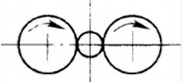
During skew rolling, the rotation direction of the work roll is the same, and the longitudinal axis of the rolling piece is in a certain direction slope. In the production of aluminium alloy pipes and some special-shaped products, two-roll or multi-roll skew-rolling is often used. According to different roll systems, aluminium alloy rolling can be divided into two-roll rolling, multi-roll rolling and special roll rolling (such as planetary rolling, V-shaped rolling, etc.) rolling: according to different roll shapes, aluminium alloy rolling can be divided into flat roll rolling and grooved roll rolling. According to different product varieties, aluminium alloy rolling can be divided into plate, strip, foil rolling, bar, flat bar and special-shaped section rolling, pipe and hollow section rolling, etc.
Skew rolling
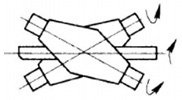


B. Extrusion
Extrusion is a kind of ingot that is loaded into an extrusion cylinder, and the metal is pressed through an extrusion shaft to extrude it from a die hole of a given shape and size to produce deformation to obtain the required extruded product processing methods. According to the directions of metal flow during extrusion, extrusion can be divided into forwarding extrusion, reverse extrusion and side extrusion.
During forwarding extrusion, the movement direction of the extrusion shaft is consistent with the flow direction of the extruded metal, while during reverse extrusion, the movement direction of the extrusion shaft is opposite to the flow direction of the extruded metal. According to the heating temperature of the billet, extrusion can be divided into hot extrusion and cold extrusion. In hot extrusion, the ingot is heated to a temperature above the recrystallization temperature for extrusion, and cold extrusion is extrusion at room temperature.




C. Drawn
Drawn is that the drawing machine pulls the aluminium and aluminium alloy blanks (wire blanks or tube blanks) from the die L of a given shape and size through the clamp, so as to produce deformation and obtain the required processing methods of tubes, rods, shapes and wires. According to the different types and shapes of the products produced, drawn can be divided into wire drawing, tube drawing, bar drawing and profile drawing.
Pipe drawing can be divided into air-drawing, core-end drawing and floating core-end stretching. The main elements of drawing processing are the drawing machine, drawing die and drawing reel. According to the drawing mould, it can be divided into single-mode drawing and multi-mode drawing.
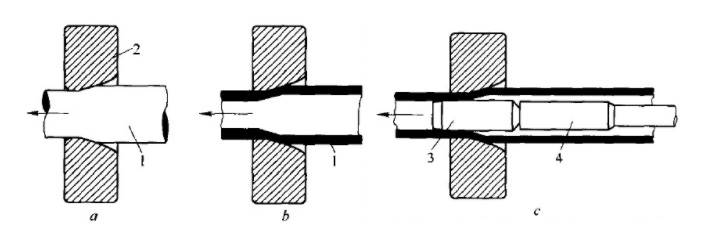

D. Forging
Forging is a processing method in which a forging hammer or indenter (mechanical or hydraulic) applies pressure to aluminium and aluminium alloy ingots or forging billets to cause deformation of the metal. There are two basic methods for aluminium alloy forging: free forging and die forging. Free forging is to put the workpiece in a flat anvil (or anvil) for forging; die forging is to put the workpiece in a die of a given size and shape, and then apply pressure to the workpiece to forge deformation, and obtain the required die forging.
Forging repair process
Repairing is an important part of the aluminium alloy die forging process. Because the aluminium alloy is soft at high temperature, has a high viscosity and poor fluidity, it is easy to stick to moulds and produce various surface defects (folds, burrs, cracks, etc.). Before the next process, it must be polished and cleaned to remove surface defects, otherwise, the defects will be further enlarged in the subsequent process, and even cause the forging to be scrapped.
Tools used for repairing include pneumatic grinders, pneumatic milling cutters, electric milling cutters and flat spades. Before repairing, check the defective parts by corrosion. The repaired part should be smoothly transitioned, and its width should be 5-10 times of the depth.
(2) Classified according to the temperature characteristics of the product
A. Hot processing
Hot processing refers to the forming process of aluminium and aluminium alloy ingots above the recrystallization temperature. During hot processing, the ingot has higher deformation performance and lower deformation resistance, and products with larger deformation can be produced by equipment with smaller capacity. In order to ensure the structure and performance of the product, the heating temperature, deformation temperature and deformation speed of the workpiece, the degree of deformation, the end temperature of deformation and the cooling rate after deformation should be strictly controlled. Common aluminium alloy hot processing methods include hot extrusion, hot rolling, hot forging, hot upsetting, liquid forging, semi-solid forming, continuous casting and rolling, continuous casting and rolling, continuous casting and continuous extrusion.
B. Cold processing
Cold processing refers to the forming process completed below the recrystallization temperature that does not produce recovery. The essence of cold processing is the combination of cold working and intermediate annealing. Cold processing can obtain final products with a smooth surface, accurate size, good structure and can meet different performance requirements: the most common cold processing methods are cold extrusion, cold head forging, cold rolling of pipes, cold drawing, cold rolling of strip and foil, cold stamping, cold bending, spinning, etc.

C. Warm processing
Warm working is a forming process between cold and hot processing. The main purpose of warm processing is to reduce the deformation resistance of metals and improve the deformation properties (workability) of metals: the most common warm processing methods include warm extrusion, warm rolling, warm head forging, etc.
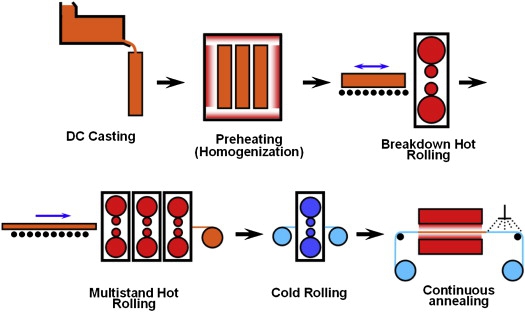
Main differences between hot rolled and cold rolled aluminium plates:
Different usage: cold-rolled aluminium plates are mostly used for moulds, and hot-rolled aluminium plates are suitable for stamping and drawing.
Different properties: the surface quality of hot-rolled aluminium plates is good, and the mechanical properties and ductility are strong, and the oxidation effect is good. At the same time, the processed aluminium circles are generally processed from aluminium plates, which are naturally affected by the properties of aluminium plates.
The supply of raw materials is different: The hot-rolled billet is vertically cast into billet-heated-rolled into coils for cold rolling, and the cold-rolled billet is cast-rolled coil-continuous casting rolling.
The production process is different: cold rolling is processed by a casting machine into cast rolls (8mm thickness) and processed by a cold rolling machine, while hot rolling is heated by an aluminium ingot (400-500mm thickness), which is heated at high temperatures, rolled by the hot rolling mill.
RELATED NEWS
- O+ Tower Project Showcases Our Production Prowess 2025-02-20
- Guangdong Aluminum Association and Moscow University Business School visited Gua 2024-12-12
- Guangdong Aluminium Association International Trade Co., Ltd. signed an overseas 2024-11-21
- Guangdong Aluminum Association International Trade Co., Ltd. Participates in the 2024-11-15
- Simplified Approach to Spandrel Area Treatment in Curtain Wall Glazing 2024-10-25
CATEGORIES
LATEST NEWS
CONTACT US
Contact: Manager:Miss Jasmien
Phone: +8618825429836
E-mail: info@gdaa-cn.com
Whatsapp:+8618825429836
Add: Headquarter:No.8,Yixian Road,GDAA Mansion,Guangfo Zhicheng, Dali Town,Foshan,Guangdong.China
